Prediction of proteasome cleavage sites
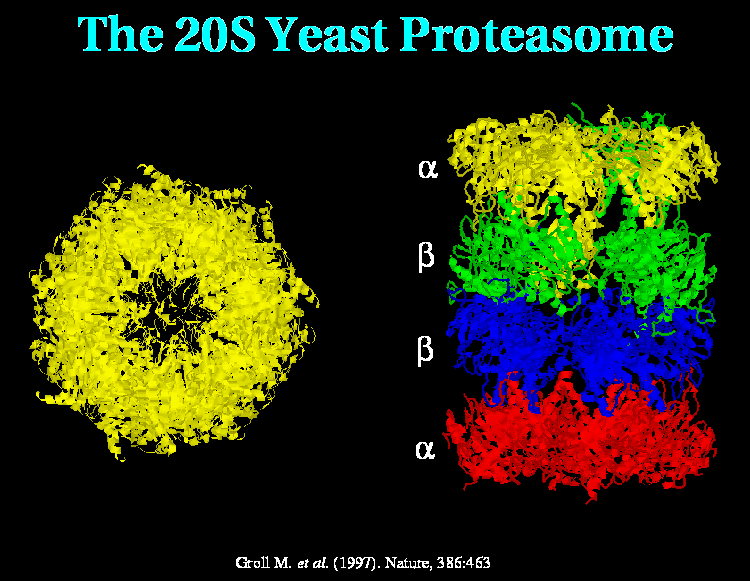 Yeast proteasome picture- Groll M., et. al. (1997) Nature 386:463 PDB code 1RYP
Yeast proteasome picture- Groll M., et. al. (1997) Nature 386:463 PDB code 1RYP
Proteasomal cleavage of proteins is the first step in the processing of most
antigenic peptides that are presented to cytotoxic T cells. Still, its specificity
and mechanism are not fully understood. To identify preferred sequence
signals that are used for generation of antigenic peptides by the proteasome,
we performed a rigorous analysis of the residues at the termini and flanking
regions of naturally processed peptides eluted from MHC class I molecules.[Altuvia et. al. 2000]
Our results show that both the C terminus (position P1 of the cleavage site)
and its immediate flanking position (P1') possess significant signals. The N
termini of the peptides show these signals only weakly, consistent with
previous findings that antigenic peptides may be cleaved by the proteasome
with N-terminal extensions. Nevertheless, we succeed to demonstrate
indirectly that the N-terminal cleavage sites contain the same preferred
signals at position P1'. The signals found at the P1 and P1' positions of the cleavage site can be translated to a cleavage score which can estimate the cleavage potential of positions along the sequence. nice-cut.tab scores.html
Copyright ©, 1997, The Hebrew University. All Rights Reserved

